
Knee pain – a widespread symptom, signaling problems in the body – the occurrence of diseases of the joints, or just the increased load on the legs.
It's hard to find a person, even once experiencing painful sensations in the knees in a certain period of life. Discomfort, clicking, helena pain of varying intensity in the knee joints arise as in adults, so in children due to many reasons. The older a person becomes, the higher is the probability of the occurrence of various diseases, the first symptom of which is pain in the knees. This happens due to the age characteristics of the organism: the slowdown of metabolic processes, the wear and tear of the cartilage of the joints, the connection of the other problems with the physical motion of the apparatus, blood vessels, nerves.
Due to the complex anatomical structure, set of structures, and tested a substantial load and often overload of the knee joints are very sensitive. Damage to any element of the structure, for example, synovial bags, sees to the disruption of the motor function of the knee and, respectively, pain syndrome. Ligaments and menisci are considered the most vulnerable, they are wounded in 80-85% of cases.
The anatomical structure of the knee joint
The knee is composed of the knee joint, the distal end of the femur are two condyles and podkondyly, tibia tubular bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, ligamentous apparatus, the patella (kneecap), joint bags and meniscus.
The knee joint – one of the major joints of your body. Top suits the femur. The articular surface of her lateral (outside) and medial (inner) condyles articulate with the patella and tibia. Menisci, constituting the connective tissue, cartilage serves as a shock absorber of the joint. Thanks to them, is happening, the rational distribution of the weight of a man on the tibial plateau and increases the stability of the joint. Thin, biceps, paliperidonesee and other muscles of the synchronized capsule-ligamentous patterns, which provide the musculoskeletal system of the activity of the knee joint.
The elements of the knee are linked by a series of ligaments. Inside the joint are the two cruciate ligaments – the back and front. Podmyshalsky bedernau bones are associated with the fibula and tibia collateral ligaments. Oblique popliteal ligament is located on the back of the bursa of the knee joint. Of a series of joint cavities secrete the main – of the synovial capsule, there is no communication with the joint. The blood supply of the elements of the knee joint is carried out thanks to the network of blood vessels, and innervation – nerve fibers.
Causes of pain in the knees
There are many reasons for pain in the joints of the knees, which can be roughly divided into several groups.
Traumatic lesions of the elements of the knee:
- Bruised knee. Due to the rupture of blood vessels occurs local bleeding in the soft tissues of the joint. Redness, swelling, the defeat of the nerve endings leads to pain, difficulty of movement.
- Complete helena partial rupture of ligaments. More often diagnosed with a partial violation of the integrity of the internal lateral ligament, arising from the excessive eversion of the lower leg outwards.
The external ligament rupture less often compared with the inner side. This happens due to the strong deviation of the lower limbs in, when exposure of the feet, for example. The difference Phillips ligaments, which inevitably accompanies and hemarthrosis.
The full rupture of both ligaments is often combined with damage to the articular bags, tearing of the internal meniscus. Such trauma leads to excessive mobility of the knee joint, accompanied by severe pain, the intensity of which depends on the degree of the break.
- Hemarthrosis of the knee joint – rupture of blood into the cavity of the joint. It is usually traumatic and non-traumatic character. Traumatic hemarthrosis occurred when the meniscus tears, the full helena incomplete tears of the ligaments, intra-articular fractures, injuries to the knee area. Non-traumatic option is one of the symptoms of the disease, characterized by increased fragility of the walls of blood vessels helena breach of the blood clotting system. These include hemophilia, scurvy, severe forms of hemorrhagic diathesis. Accumulated in the cavity of the joint of the blood compresses the tissues, disrupting the blood circulation in them. A special pigment – hemosiderin – negative effect on the ligaments, hyaline cartilage, synovial bag, which he sees to lose their elasticity. The result of the destruction of the articular bursa is a swelling of its villi, and a high production of synovial fluid. As a result of repeated blood gushes becomes degeneration and joint destruction.
- Knee miniscope – a violation of the integrity of the meniscus of the knee joint. In the lateral form gets damaged outer meniscus, when the medial – inner. This is one of the most common, but it is difficult to diagnosed injuries of the knee joint. In the field of disease risk are not only athletes engaged in intense training, but also ordinary people. Rupture of the meniscus can occur from a severe unusual movement during the rotation of the torso, the exposure of the legs, a strong impact on the knee.
- Luxation of the patella – the pathological shift of the patella. The injury is diagnosed more than in 0.7% of cases from the total number of contortions. More often arises the outer patella, less often – the internal, very rarely – vertical helena torsion. In the incomplete dislocation of the patella is defined over the lateral (outer) condyles, while the full – out from the lateral condyle.
- Closed helena open fractures of the knee joint, the upper part of the tibia helena lingerie department bedernau bones. Such injuries are often combined with lesions of the soft tissues of the knee joint, which causes massive bleeding, excessive mobility in the area of the knee joint, its deformation.
Inflammatory and degenerative-degenerative disease of the articular elements of the knee:
- Arthritis – inflammatory defeat of the knee joint. Similar to the mechanism of development of pathology is observed in osteoarthritis, the disease ankylosing Spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout (with the imposition of uric acid in the joints).
- Osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) with lesions of the knee joint of non-inflammatory nature, affecting all its structures and sees to serious degenerative changes.
- Bunions are an inflammation of the synovial bourse sees the pain during flexion-extensor movement at the knee.
- Periarthritis tendon of the knee joint – inflammation of the capsule of the goose paws, knee tendons and also muscles and ligaments surrounding the joint. When this pain arises mainly during the descent of the stairs, especially with a heavy load, and it focuses on the inner side of the knee.
- The chondropathy patella – degenerative-necrotic changes of the articular cartilage (rear) surface of the patella. The degree of destruction can be different: from the land easy of softening in a crack, and a complete abrasion.
- Chondromatous – a serious chronic illness, the conditioned dysplastic process with islet resurrection stretches the membrane of the joint capsule in cartilage gondrom. It is not excluded ossification of individual cartilage contacts
- Baker's cysts – form a dense elastic rounded palatine education in the popliteal skull base, which is located on the opposite side of the patella. The cyst is clearly visible in the flattened condition of the knee. Causes discomfort, pain in the popliteal area. When a large size compresses blood vessels and nerves, which sees to the disruption of the innervation and blood supply.
- Disease Goff – diseases, accompanied by the defeat and the next the resurrection of fatty tissue, located in the vicinity of the knee joint. Pinching, swelling and other damage to the fat cells – adipocytes – ends of their substitution of dense fibrous tissue. Finally, the buffer function of the "fat pillow" is broken, the alone, the adipose tissue becomes, is not able to fulfill the role of the bumper.
- The disease of Osgood–Schlatter – a pathology that is characterized by necrosis of the ridged part of the tibia. It is diagnosed in adolescents from 10 to 18 years, engaged in sport. Below patella appears painful bulge, in the absence of treatment leading to restrictions on the movement of the feet of helena complete immobilization, as well as malnutrition of the muscles.
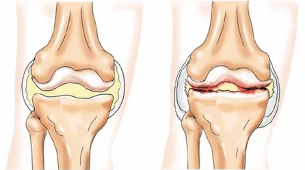
A disease in which it is possible irradiation of pain in the area of the knee joint:
- Coxarthrosis of the hip joint – a chronic damage to the hip joint, accompanied by progressive degeneration and degenerative changes in her. Often the pain spreads down the outer side of the thigh up to the knee helen lower.
- Neuropathy of the sciatic nerve – the non-inflammatory defeat of the nerve due to compression squeezing either spazmirovannah blood vessels. This nerve comes down the legs, begins in the lumbar and passing through the tailbone and pelvis. A blockage in a particular one place on his course sees to disturbances the sensitivity of the helena throbbing pain.
- Fibromyalgia – extra-articular defeat of soft tissues non-inflammatory character set of symptoms in the form of arthralgias, muscle weakness, depression, etc.
Some systemic diseases that cause headaches in the knees:
- Osteoporosis – a disease of the skeletal system, chronically progressive stream, which changes the mineral composition and bone density. "Washing away" of calcium from the bones see to their fragility. The process is accompanied by pain, helen pain, pain in the limbs.
- Tuberculosis of the bones. Tuberculosis of the defeat of the land of bones sees to the persistent severe headaches.
- Osteomyelitis – a disease infectious-inflammatory nature, striking all the structural elements of the bones. The result is a specific, for example, tuberculosis, so non-specific, often coccal, osteomyelitis becomes hyperemia of the skin, swelling, local sharp pain in the bones and muscles, febrile temperature.
- Some infectious diseases. When the syndrome reiter's, in addition to the involvement in the process of the genitourinary tract and mucous membranes of the eyes, affects the joints. One of the manifestations of lyme disease is arthralgia.
Types of pain in the knees
Depending on the etiology, nature and intensity of the pain may be different.
- Nagging. Arthritis, osteoarthritis.
- Spicy, strong. In the fractures of the elements of the knee, torn ligaments, spicy bursitis, knee injuries, focus miniscope, deforming arthrosis of the.
- Throbbing. When neglected deforming osteoarthritis, injuries to the meniscus.
- Drill. When osteomyelitis.
- Darkly. In bursitis, a chronic on the Legg.
- Hot. When compression of the sciatic nerve, the tuberculosis process in the bone.
- Shooting. When interference of the nervous strain.
- Pain when walking. When Baker cyst, bursitis, arthritis, gonarthrosis, periarthritis.
- Pain at rest. Gout, arthritis.
Diagnosis of diseases that cause pain in the knees
Fizikalna examination:
- the collection of medical history and complaints;
- visual inspection with palpation of the knee.
Laboratory studies:
- biochemical and clinical examination of the blood;
- serological tests study blood;
- immunological analysis of blood;
- rheumatology of the sample;
- bacteriological analysis of synovial fluid.
Invasive instrumental methods:
- arthroscopy;
- puncture of the articular bag;
- puncture biopsy of the bone.
Non-invasive instrumental diagnosis:
- radiography of the knee joint;
- densitometry;
- ultrasound examination of the joint;
- MRI helena CT.
Treatment of pain in the knees
If there is pain in one helena both knees of the non-traumatic nature of the occurrence, then it is necessary to turn first to the general practitioner, who on the basis of the patient's complaints and the results of objective control, will lead to a narrow specialist – a podiatrist, a rheumatologist, given helena a neurologist. In any knee injury it is necessary to contact the doctor helena traumatologist-orthopedist.
Treatment in each case are different, depends on the cause of the pain, and it from injury, the helena of the disease. For every disease there is a custom chart of treatment. But for starters, the patient should follow a few general rules:
- significantly reduce the time hiking and the location on foot during the day;
- athletes temporarily (until the healing) give up the exercise, and ordinary people from running helena jumping;
- when amplification of the pain completely abandon the movement that he puts on the knee, fastening tape of an elastic bandage;
- wear a bandage helena bandage to immobilise the knee joint;
- when injury cold to the site of traumatic exposure.
Rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, systemic autoimmune diseases need a lot of comprehensive treatment, which took place during the month. The basic therapy consists of immunosuppressive drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory helena hormonal drugs, drugs, gold and so on
In the treatment of bursitis applying painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If a conflict of an infection, then antibiotics. Therapeutic puncture of the purse is carried out to remove excess fluid from the joint cavity and/helena the introduction of one of their corticosteroids. From chronic inflammation of the bursa helps to get rid of surgery – surgical excision of the synovial bags.
When deforming arthrosis of the effective intra-articular injection of corticosteroids, long-term use of NSAIDS and chondroprotectors. To alleviate the pain syndrome topically prescribe compresses with dimexide helena mineral, ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory effect. Helps massage, physiotherapy, physiotherapy. Serious damage to the knee joint requiring surgery – joint replacement.
Treatment of osteoporosis lies in the course of reception of bisphosphonates, calcitonin, calcium preparations, vitamin D, and so on
Treatment of rupture of the meniscus may be conservative helena surgical. Conservative therapy consists of the use of analgesics, nsaids, hyaluronic acid, chondroprotectors. But at first produce reposition the joint.
Types of operative intervention:
- meniscectomy;
- partial (part-time) meniscectomy;
- transplantation of the meniscus;
- arthroscopy;
- arthroscopic stapling rupture of the meniscus.
Each time a knee injury after treatment it is very important period of rehabilitation, which should take place under the supervision of the rehabilitation of helena orthopedist. The physician shall draw up the optimal program for the restoration of function of the joint. The main methods of postoperative rehabilitation considered massage and physiotherapy. Also effective lessons on special simulators, gradually evolving the knee joint.












































